
ATOMS AND NUCLIDES
NUCLEAR CLOCKS
RARE PARTICLES AND THEIR DETECTION
AREAS OF RESEARCH
Archaelogy
Astrophysics
Enviromental and Geophysical Research
Biomedical Tracing
Review article
ATOMS AND NUCLIDES

Matter, as we understand it, is composed of a hierarchy of building blocks. Living creatures, as well as our inanimate surroundings, are made of molecules, which in turn are made of atoms, whose mass resides almost entirely in the nuclei. The nuclei include protons and neutrons, which ultimately consist of quarks and gluons. On the microscopic scale of the natural elements, the building blocks of matter are elegantly classified in three major schemes :
- the Periodic Table of Elements
- the Chart of the Nuclides, (Poster)
- the Standard Model of the Fundamental Particles.
The question "when and how did it all start" is partly answered, to our present understanding, by the Big Bang model.
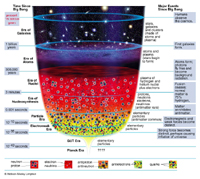
It is for example fascinating to realize that some of the light elements, say hydrogen, helium, lithium, which we observe today in Nature, were produced (or more exactly their nuclei were) about three minutes after the Big Bang. Around us on Earth, the light isotope of helium (3He) is largely "primordial" in this sense. The case of helium on Earth is actually interesting : its more abundant isotope (4He) is continuously created by natural radioactivity (alpha) and this "radiogenic" 4He is added on Earth to the primordial 4He.
This brings about related questions :
when were all other elements created or "synthesized"?
Are some of the nuclei we are made of "primordial" in any sense ?
Are nuclei still synthesized today by Nature ?
Are there other "radiogenic" nuclides, or otherwise produced ?
Is there some information on time or age, embedded in Nature and its nuclei, be it
on cosmological, galactic, geologic, prehistorical or historical time scales ?
Can we reveal such information ?
Our research, extending to several disciplines, is devoted to these questions.
NUCLEAR CLOCKS
The stable nuclides which constitute matter as we know it, ourselves, our computer chips, the planets around us, have been synthesized in the stars of our Galaxy. Myriads of stars of our Galaxy may have contributed to produce the atoms we are made of. This is in principle possible since once a stable nuclide has been produced, it is not likely to disappear. Stable nuclides are insensitive to time.
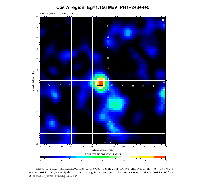
On the other hand, unstable nuclei, which decay via the various radioactivity processes, constitute physical clocks : the very presence of an unstable nuclide indicates that it must have been produced, and no matter how, at most a few half-lives ago. In some cases, the relative number of such nuclides will act as a clock with a scale comparable to its half-life. Amazingly, these scales range from many million years to less than picoseconds.
Let us take two examples taken from two different disciplines.
In recent years, astronomical observations have been extended to the range of gamma radiation (at much shorter wave length than visible or UV light). It was discovered by instruments aboard spacecrafts that certain regions of the sky emit a gamma-ray known from laboratory studies to belong to the decay of the nucleus 44Ti. The half-life of this nucleus is of 60 years: this fact reveals that the nucleosynthesis of 44Ti in the observed site is very young, dating no more than a few hundred years and probably originating in a supernova explosion. The 44Ti nucleus acts here as a Galactic clock.
We have mentioned earlier the existence on Earth of "radiogenic" nuclides. They belong to a larger family of nuclides constantly produced by nuclear phenomena. An important class of such nuclides are the "cosmogenic" nuclides, produced by interaction of cosmic ray with matter.
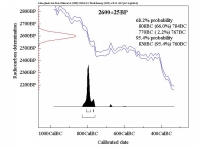 The most popular of these is radiocarbon 14C. Produced in the Earth atmosphere
by cosmic rays, it reaches (as carbon dioxide gas) the important reservoirs of Earth
(oceans, biosphere). With a nuclear half-life of 5730 years,
the 14C content of a material (if it is not replenished) will decrease by
1 % every 83 years ! Under certain circumstances,
we have here the principle of an archaeological or historical clock.
Radiocarbon dating, discovered by Libby in 1945, has been ever since a major dating tool for archaeology.
The most popular of these is radiocarbon 14C. Produced in the Earth atmosphere
by cosmic rays, it reaches (as carbon dioxide gas) the important reservoirs of Earth
(oceans, biosphere). With a nuclear half-life of 5730 years,
the 14C content of a material (if it is not replenished) will decrease by
1 % every 83 years ! Under certain circumstances,
we have here the principle of an archaeological or historical clock.
Radiocarbon dating, discovered by Libby in 1945, has been ever since a major dating tool for archaeology.
Nuclei, beyond the mere interest in their physical structure and in the way they decay or interact, occupy a tremendous importance in our quest to understand the past. None of the other building blocks of matter plays this role.
RARE PARTICLES AND THEIR DETECTION
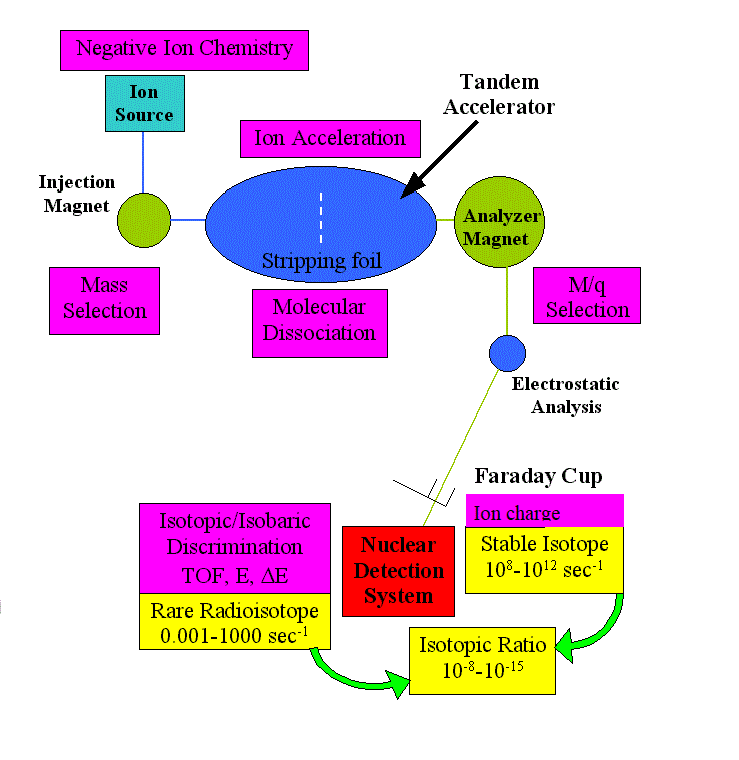
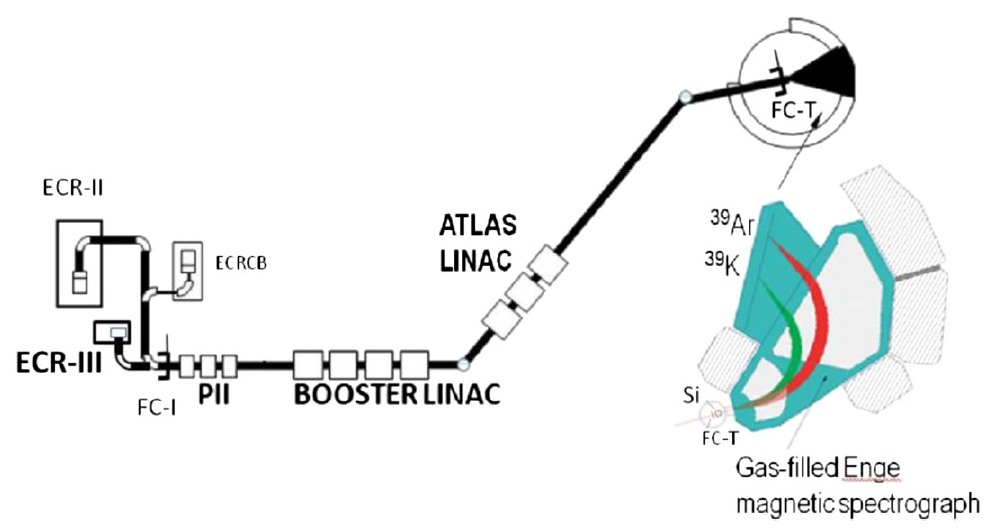
We describe here in general terms the experimental method we use to detect and "count" very rare atoms or particles, such as the cosmogenic nuclides we discussed above. Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS), a sophisticated detection technique,identifies and counts rare atoms, such as radiocarbon and other cosmogenic nuclides, at an unprecedented level of sensitivity.
Our group has been a world leader in the development of the technique and new applications. Through these efforts and those of other laboratories, AMS is now accessing radionuclides with half-lives ranging up to million years as geophysical chronometers or environmental tracers.
The method links techniques of particle acceleration, mass spectrometry, nuclear identification and computer data analysis.
A series of sophisticated filters are applied, based on different physical and chemical to discriminate a desired species from the background matrix : ion source chemistry, physical dispersion by magnetic and electrostatic elements, molecular dissociation.
The main component of the experimental apparatus is a particle accelerator, called Tandem Accelerator and the superconducting linear accelerator ATLAS at Argonne National Laboratory.
AREAS OF RESEARCH
Nuclear Astrophysics

The stable nuclides which form matter around us have been synthesized in stars and followed a long itinerary in interstellar space until their eventually merging into a nebula and condensing into the Solar System. The time of this formation is about 4.5 billion years ago, which we know from the decay of radioactive nuclides such as uranium and thorium isotopes. These long-lived nuclides, as of course the stable ones, are still around us. Shorter-lived nuclides, present in the Early-Solar matter, have decayed and are now extinct.
However, the Interstellar Medium (ISM), present in the Galaxy, resembles in many aspects the Proto-Solar nebula and is expected to contain "freshly" synthesized nuclides. It is now known that grains of ISM penetrate into the Solar System and such grains have even be detected in the higher atmosphere of the Earth. They may therefore reach the Earth and give us the amazing possibility of studying matter of an unknown kind.
We are presently pursuing a search for such material in Earth reservoirs such as deep-sea sediments and nodules where the possible accumulation of ISM accreted material may be detectable. The unmistakable signature for such material would be the presence of "short-lived" nuclides extinct in the present Solar System : candidates for such nuclides are 244Pu (81 Myrs), 247Cm.

This research is a collaboration between the Racah Institute, Argonne National Laboratory (USA), Australian National University and University of Notre-Dame (USA).
Enviromental and Geophysical Research
1. Environment
Detection of naturally occurring and artificial nuclides is of wide-ranging interest in geophysical and environmental sciences. It is observed that the nuclide 129I for example, has increased in concentration in the environment by several orders of magnitude in the last forty years, due to nuclear power and nuclear reprocessing plants. The first measurements of environmental 129I were performed by our group at the Racah Institute, following the nuclear reactor accident of Chernobyl in 1986. Concentrations of 129I in marine seaweeds collected along the Mediterranean Israeli Coast and Red Sea coast act as a monitor of global pollution transport.
The rare 236U isotope of uranium is considered as an integrating neutron monitor over the last 100 million years in geological sites. In uranium minerals, it is naturally produced in the capture by 235U of a neutron. 236U is also abundantly produced in nuclear reactors and can be used in nuclear safeguard programs for the monitoring of nuclear activity.
This research is a collaboration between the Racah Institute and Soreq NRC (Yavne, Israel), sponsored by the International Atomic Energy Agency (Vienna).
2. Geophysics
 Noble gases occupy a special place in geophysics because of their
chemical inertness. There exist a small number of cosmogenic isotopes
of noble gases which can in principle be used for dating geophysical
processes. Two cases which we are investigating at present are 81Kr
(T1/2 = 210,000 years) and 39Ar (269 years). These isotopes are
created in the atmosphere by interaction of cosmic-ray particles. Their
chemical and geochemical inertness ensure that once produced in the
atmosphere, they will follow a geochemical path (for example the
hydrological path) without being fixed in chemical compounds or
adsorbing to rocks.
Noble gases occupy a special place in geophysics because of their
chemical inertness. There exist a small number of cosmogenic isotopes
of noble gases which can in principle be used for dating geophysical
processes. Two cases which we are investigating at present are 81Kr
(T1/2 = 210,000 years) and 39Ar (269 years). These isotopes are
created in the atmosphere by interaction of cosmic-ray particles. Their
chemical and geochemical inertness ensure that once produced in the
atmosphere, they will follow a geochemical path (for example the
hydrological path) without being fixed in chemical compounds or
adsorbing to rocks.
The case of 81Kr is particularly appealing because its half-life allows in principle the dating of water (for example ground water aquifers) in the scale of hundred thousand years) by comparing the 81Kr content of the aquifer with that of contemporary water. The scheme has been applied for the first time to the Great Australian aquifer and dates of ground waters have been obtained.
In a different scale of time (hundreds of years), 39Ar is used to date ocean water samples from various origins. The age of water is an important input in the modeling of oceanic transport, a mechanism which influences heavily the global climate.
Experimentally, the cosmogenic noble gases pose different and difficult problems of detection, due to their very low abundances and to the fact they require very large accelerators of a different type than used in other AMS analysis. These experiments have been performed at the National Superconducting Cyclotron (USA) and at Argonne National Laboratory (USA).
This research is a collaboration between the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory (Columbia University, USA), the University of Vienna, Argonne National Laboratory, the National Superconductive Cyclotron Laboratory (USA), and the Racah Institute.
Biomedical Tracing
The ability to count atoms rather than the decay radiation of radioactive nuclides is triggering a major breakthrough in the use of tracers in biomedicine. Tracers consist in an amount of material added to a biological system in order to follow its biochemical evolution. Radioactive tracers are conventionnally used for the ease of detection of their decay radiation (e.g. gamma rays, positrons) in scanners and X-ray radiography.
The AMS atom counting method described above, offers several advantages : (i) since the detection capability is independent of the radioactive half-life, tracing with very long-lived nuclides becomes possible over unlimited periods of time; (ii) the sensitivity of the detection permits tracing the evolution of an element using a minute amount of tracer, not modifying the normal load of the element in a biological system; (iii) no collateral radiation risk exists due to the combination of minute amount of tracer and the long radioactive half-life.

We performed a pilot experiment where the feasibility of calcium tracing with the isotope 41Ca is studied. The rate of bone resorption and the net long-term calcium balance are important for understanding the mechanism of onset of osteoporosis and hormonal effects. We are following the evolution of a 125 nanogram dose of 41Ca injected to a patient by monitoring the 41Ca concentration in blood and urine over time.
This research is a collaboration between the Racah Institute, Triumf Laboratory (Vancouver, Canada) and University of British Columbia (Vancouver, Canada).
Review Article
We refer for a general review of the field and recent experiments to the following article.